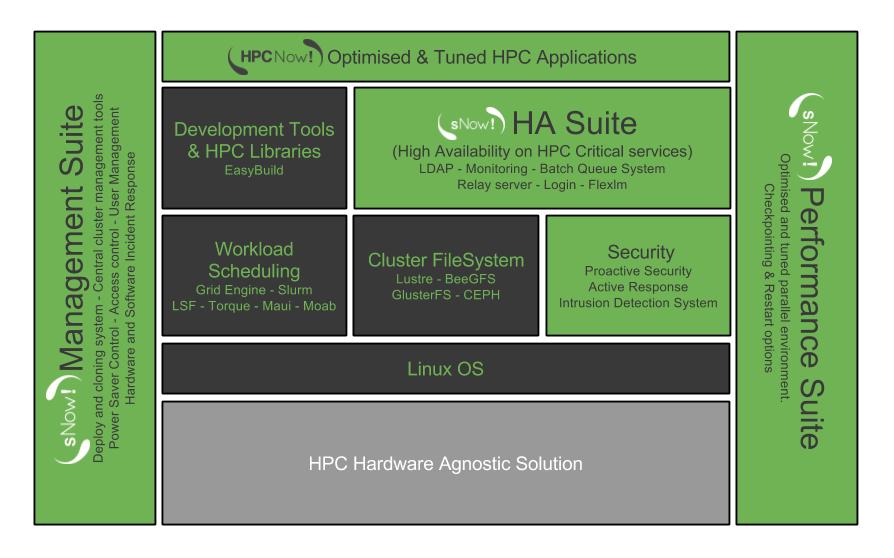
What follows is a non-exhaustive list of the most important services and technologies included.
- Xen Source for para-virtualization or Linux Containers (experimental support) for OS level virtualization.
- Shared filesystem (it uses NFS by default, but Lustre, IEEL, BeeGFS, GPFS, GlusterFS or CEPH are also compatibles.)
- Scientific Applications are managed by EasyBuild, which contains more than 500 packages and their dependencies.
- GNU/Linux distribution optimized to achieve the best performance on the compute nodes.
- Tools for the centralized installation (Kickstart, Autoyast)
- Tools for monitoring and managing the infrastructure (Ganglia, Nagios)
- Login nodes
- LDAP and Munge based authentication services
- Centralized log facility
- Batch job scheduler (i.e. Slurm, Grid Engine or Torque+Maui)
- DHCP server
This tool integrates a handful of domains (virtual machines or LXC) that provide all the critical services needed by an HPC infrastructure in an integrated environment,. The sNow! solution provides all the critical services segmented in a virtualization layer, giving flexibility and scalability to meet customer needs (fig. 1). This structure allows, for example, to control and isolate a user who is misusing the cluster without affecting the stability of the whole system.
The sNow! technology allows one to perform critical migrations without stopping the system or its services as all services can be cloned and upgraded while the original is still running. Once the upgraded clone is up and running the clients can be migrated to the new service provider without disruption. Therefore, in scenarios where the services can not be interrupted, an update of the batch queue manager or a firmware upgrade on the nodes does not require a downtime anymore, but a progressive upgrade process that can be completed in a matter of hours or weeks. The length of time would depend on on the complexity of the task to perform, the length of running jobs, and the checkpoint-restart capabilities used to migrate jobs to another node, etc.
