If you want to get involved in the development of sNow! and be able to contribute back to this project, you will need a Bitbucket account.
The official GIT repository is available here: https://bitbucket.org/hpcnow/snow-tools
The sNow! development workflow relies on a strict branching model designed around the project release. Each new feature should reside in its own branch, which can be pushed to the central repository for backup/collaboration. In order to contribute a new feature, use develop as the parent branch. When a feature is complete, it will get merged back into develop through a pull request. Features should never interact directly with master.
References
Fork sNow!
First, you’ll need to fork the sNow! repo that you want to contribute on Bitbucket. If you do not have a Bitbucket account yet, you’ll need to get one. It’s free! You should also register an SSH public key, so you can easily clone, push to and pull from your repository. We also recommend to use SourceTree Application in order to visualize and organise your git repos.
Clone your sNow! repository
Clone your fork of the sNow! repository to your favorite workstation.
git clone git@bitbucket.org:<YOUR_BITBUCKET_ACCOUNT>/snow-tools.git
Pull in the develop branch
Pull the develop branch from the main sNow! repository:
cd snow-tools
git remote add hpcnow git@bitbucket.org:hpcnow/snow-tools.git
git fetch hpcnow
git branch develop hpcnow/develop
git checkout develop
git pull hpcnow develop
Keep develop up-to-date
The develop branch hosts the latest bleeding-edge version of sNow!, and is merged into master regularly (after thorough testing). Make sure you update it every time you create a feature branch (see below):
git checkout develop
git pull hpcnow develop
Branch
Pick a branch name
Please try and follow these guidelines when picking a branch name:
- if the branch targets an issue, use the number of the issue as a prefix for your branch name, e.g.
86_for issue#86 - append a short but descriptive branch name, in which words are joined by underscores, e.g.86_encoding_scheme
Create branch
Create a feature branch for your work, and check it out
git checkout hpcnow/develop -b <NEW_FEATURE_BRANCH>
git pull hpcnow <NEW_FEATURE_BRANCH>
Make sure to always base your features branches on develop, NOT on master!
Hack
After creating the branch, implement your contributions: new features, enhancements or updates to existing features, bug fixes, etc. Make sure you commit your work, and try to do it in bite-size chunks, so the commit log remains clear.
For example:
git add snow-tools/etc/roles.d/whatever
git commit -m "New role whatever"
If you are working on several things at the same time, try and keep things isolated in separate branches, to keep it manageable (both for you, and for reviewing your contributions, see below).
Pull request
When you’ve finished the implementation of a particular contribution, here’s how to get it into the main sNow! repository. More detailed information at Atlassian Documentation.
Push your branch
Push your branch to your sNow! repository on Bitbucket:
git push origin <NEW_FEATURE_BRANCH>
Issue a pull request
If you’re contributing code to an existing issue you can also convert the issue to a pull request from the Bitbucket website. More information in this regard here.
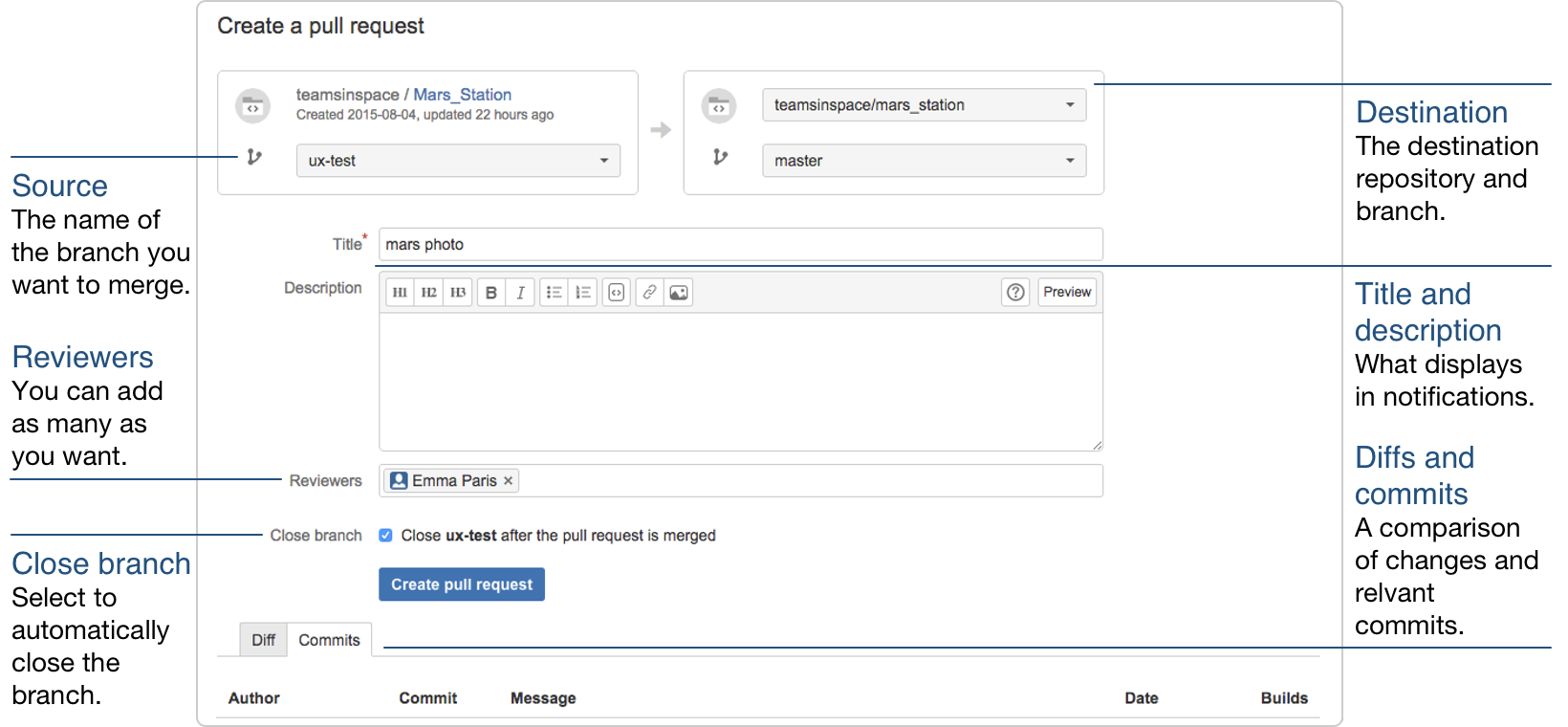
Issue a pull request for your branch into the main sNow! repository, as follows:
- go to your git repo hosted in bitbucket: https://bitbucket.org/
/snow-tools - issue a pull request (see previous screenshot) for your branch to the develop branch of the main sNow! repository.
- Add any comment you consider relevant for the development team.
Review process
A member of the HPCNow! development team will then review your pull request, paying attention to what you’re contributing, how you implemented it and code style. See Review process for contributions for more details. Most likely, some remarks will be made on your pull request. Note that this is nothing personal, we’re just trying to keep the sNow! codebase as high quality as possible. Even when an sNow! team member makes changes, the same public review process is followed. Try and act on the remarks made, either by committing additional changes to your branch, or by replying to the remarks to clarify your work.
Aftermath
Once your pull request has been reviewed and remarks have been processed, your contribution will be merged into the develop branch of the main sNow! repository. On frequent occasions, the develop branch is merged into the master branch and a new version is tagged, and your contribution truly becomes part of sNow!.
Branching strategy
The workflow used in sNow! Development is based on Gitflow, which has demonstrated a solid and strong community based collaboration. The workflow below is derived from Vincent Driessen at nvie.
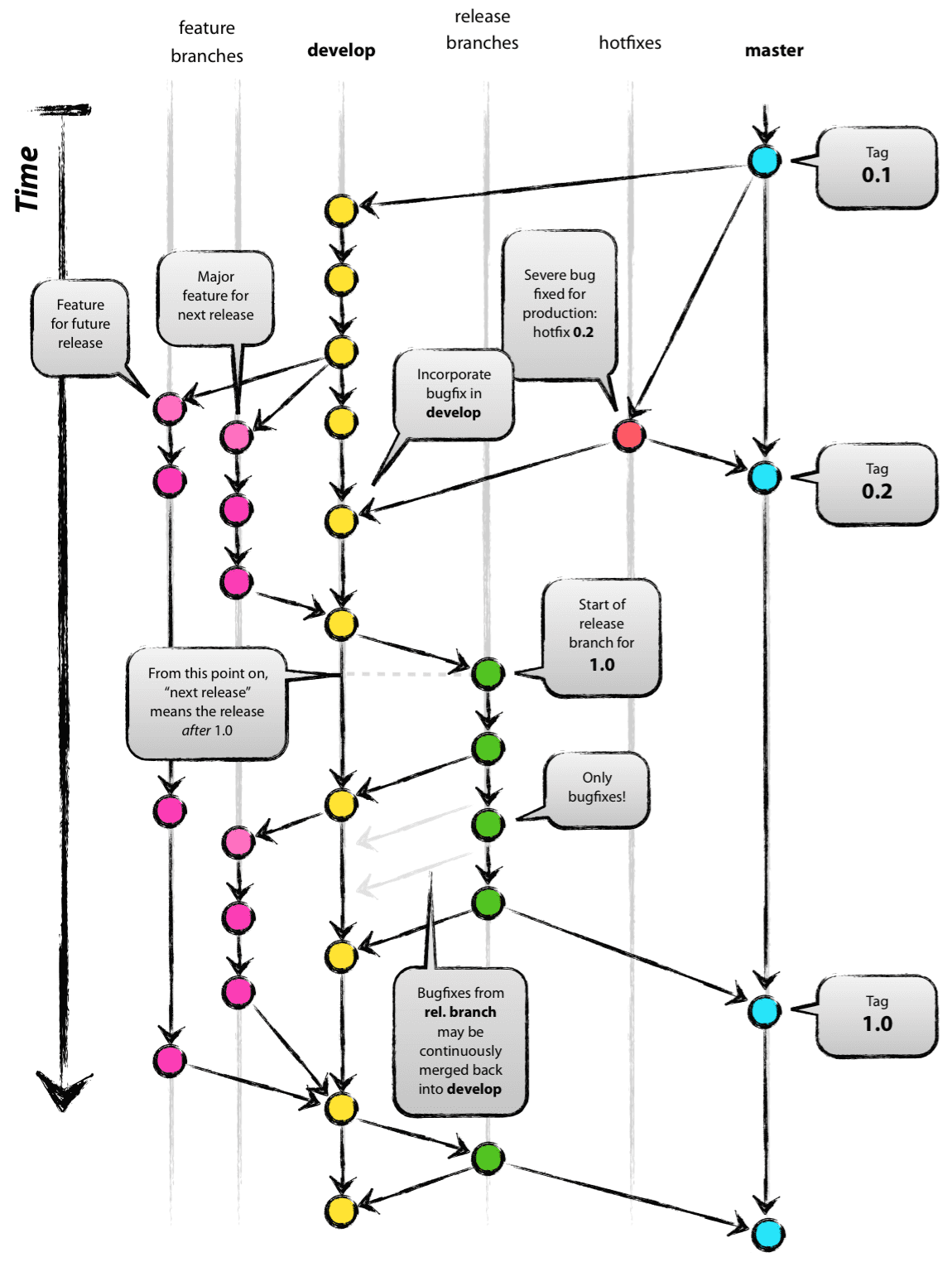
Master
This is the production branch used for deploying the releases which are identified with tags. The tags are included once the release branch (release candidate) is considered stable enough and merged into the master branch.
Develop
This integration branch is used for development. The feature branches are merged back into this branch.
Hotfix
This branch is typically used to quickly fix the production branch (master)
Feature
Used for specific feature work, Typically this branches from and merges back into the development branch (develop).
Release
This branches are used for release tasks. sNow! does not provide long-term maintenance for an specific release. Typically this branches from the development branch and changes are merged back into the development branch.
Bugfix
This branch is typically used for fixing bug againsts a release branch, which later on are also merged into the development branch.
Tags and software versioning schemes
The releases are identified with tags in the production branch (master) by following the semantic versioning. Given a version number MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH, increment the:
- MAJOR version when you make incompatible API changes,
- MINOR version when you add functionality in a backwards-compatible manner, and
- PATCH version when you make backwards-compatible bug fixes.
Additional labels for pre-release and build metadata are available as extensions to the MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH format.
Testing new features available in the development version.
In order to evaluate new features available in the development version, you only need to pull the latest changes from the HPCNow! git repository. To do so, just add the remote repo with the following instructions:
cd /sNow/snow-tools
git remote add hpcnow git@bitbucket.org:hpcnow/snow-tools.git
git fetch hpcnow
Create a new branch using the develop branch and pull the new data:
git branch develop hpcnow/develop
git checkout develop
git pull hpcnow develop
In order to roll back to the stable version, execute:
git checkout master
